Classic Pseudopelade
What is Classic Pseudopelade (Brocq)?
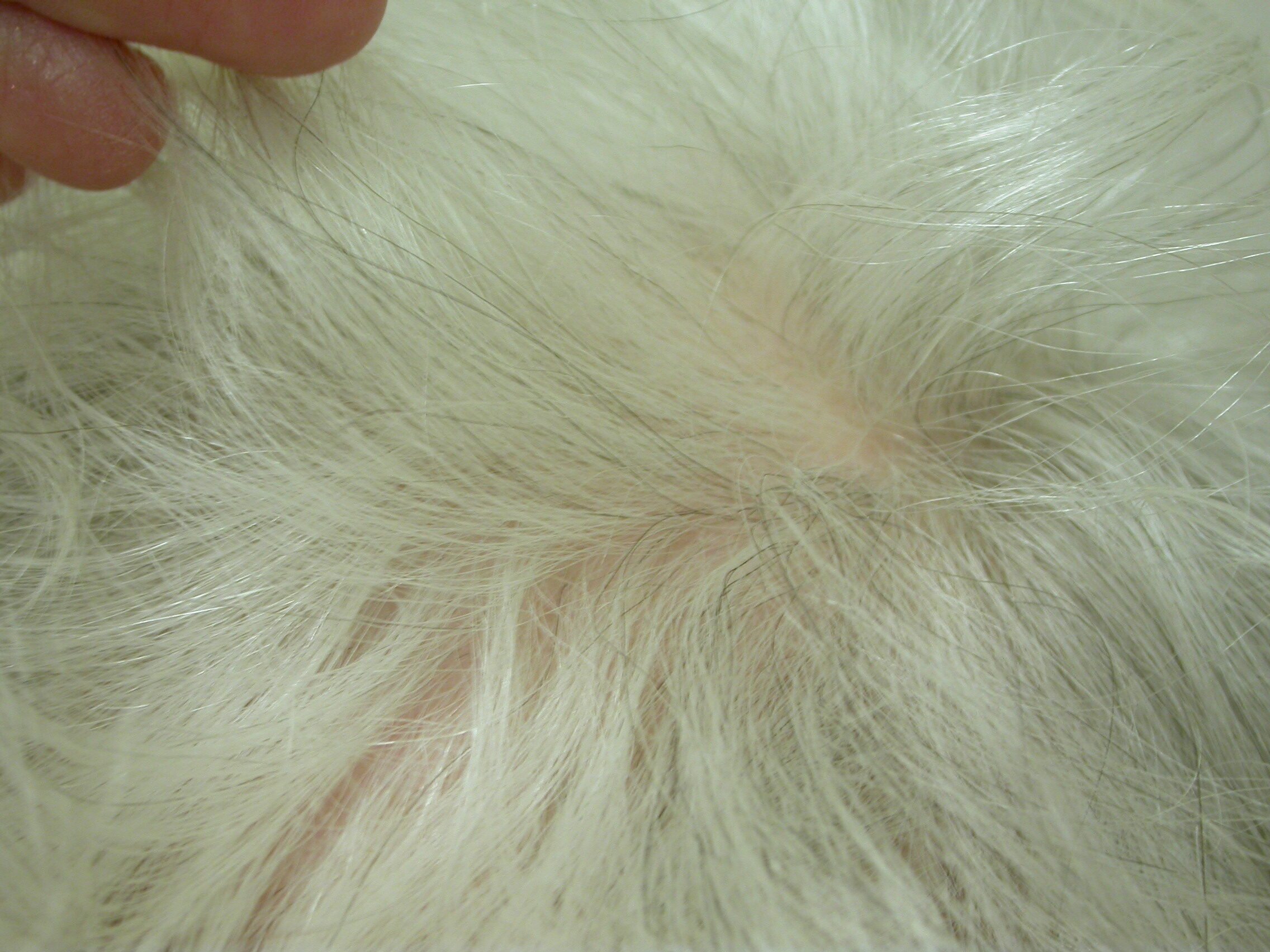
Classic Pseudopelade (Brocq) is a rare type of scarring hair loss, meaning that the hair loss in affected areas is permanent. Both men and women can develop this condition, though it is three times more common in women. The term "pseudopelade" is French for "imitator of alopecia," as it resembles non-scarring alopecia areata at first glance. However, upon closer examination, pseudopelade reveals smooth, shiny patches of hair loss without visible follicular openings. The condition has been confusing because it can describe either a new scarring alopecia without evident inflammation or symptoms or a late-stage "burnt-out" form of lichen planopilaris (LPP).
Symptoms & Causes
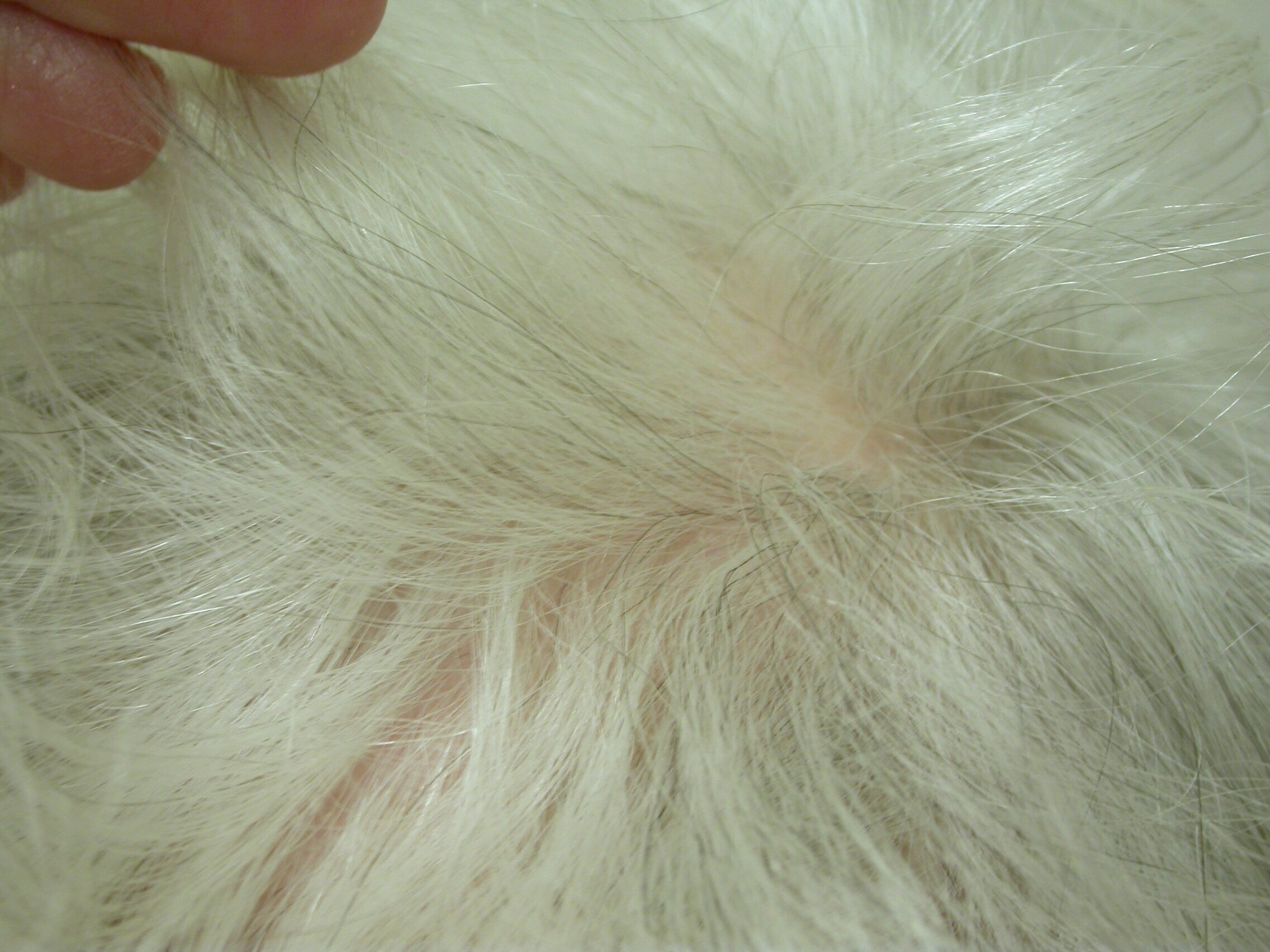
Pseudopelade of Brocq is characterized by several distinct features:
- Areas of scarring hair loss.
- Some redness around the hair follicles.
- Skin depressions.
- Biopsy findings showing minimal inflammation, loss of sebaceous (oil) glands, and scarring.
The exact cause of pseudopelade is unknown, making it a challenging condition to diagnose and treat. It may progress very slowly, even with treatment. The condition is primarily identified through clinical examination and scalp biopsy, which typically shows very little inflammation and significant scarring.
Diagnosis & Treatments
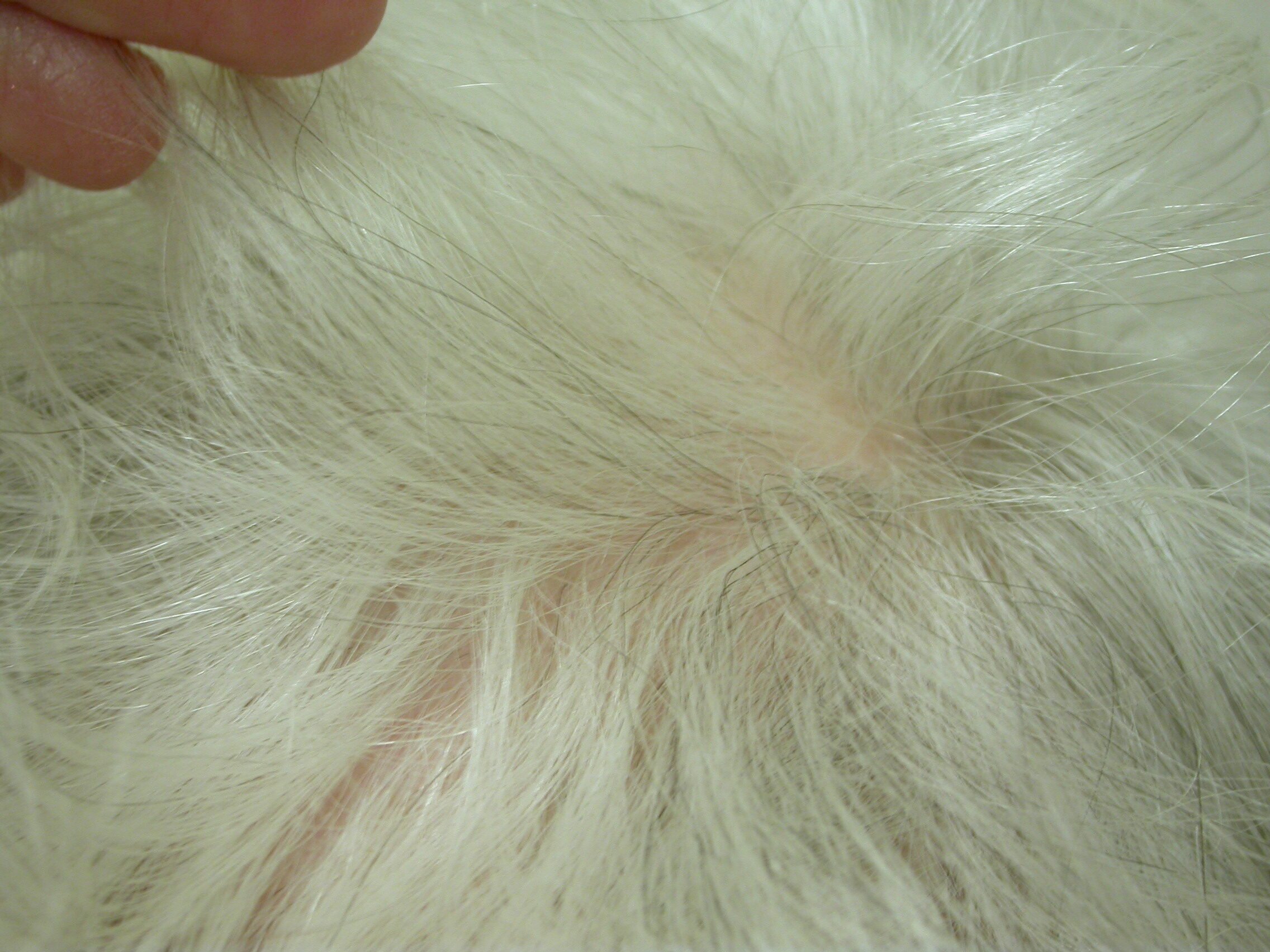
Diagnosing pseudopelade involves a detailed patient history, a thorough physical examination of the scalp, and often a scalp biopsy. Early intervention is crucial to manage the condition effectively, even though it may still progress slowly in some cases.
Treatment options aim to control symptoms and slow progression. They include:
- Oral Medications: Doxycycline, hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), isotretinoin (Accutane), and mycophenolate mofetil.
- Injections: Steroid injections may be advised to reduce inflammation in localized areas.
- Topical Treatments: Patients may be prescribed medications to apply at home, such as clobetasol, tacrolimus (Protopic), or clobetasol propionate shampoo (Clobex).
Because pseudopelade can be difficult to treat, it is essential to discuss all available options with a dermatologist. The dermatologist will tailor the treatment plan to the individual's specific symptoms and disease severity. While treatment can help manage symptoms and potentially slow the spread, the scarring and hair loss in affected areas are typically permanent. Non-surgical cosmetic options like wigs or hairpieces can also be considered to improve the appearance of hair loss.
