Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
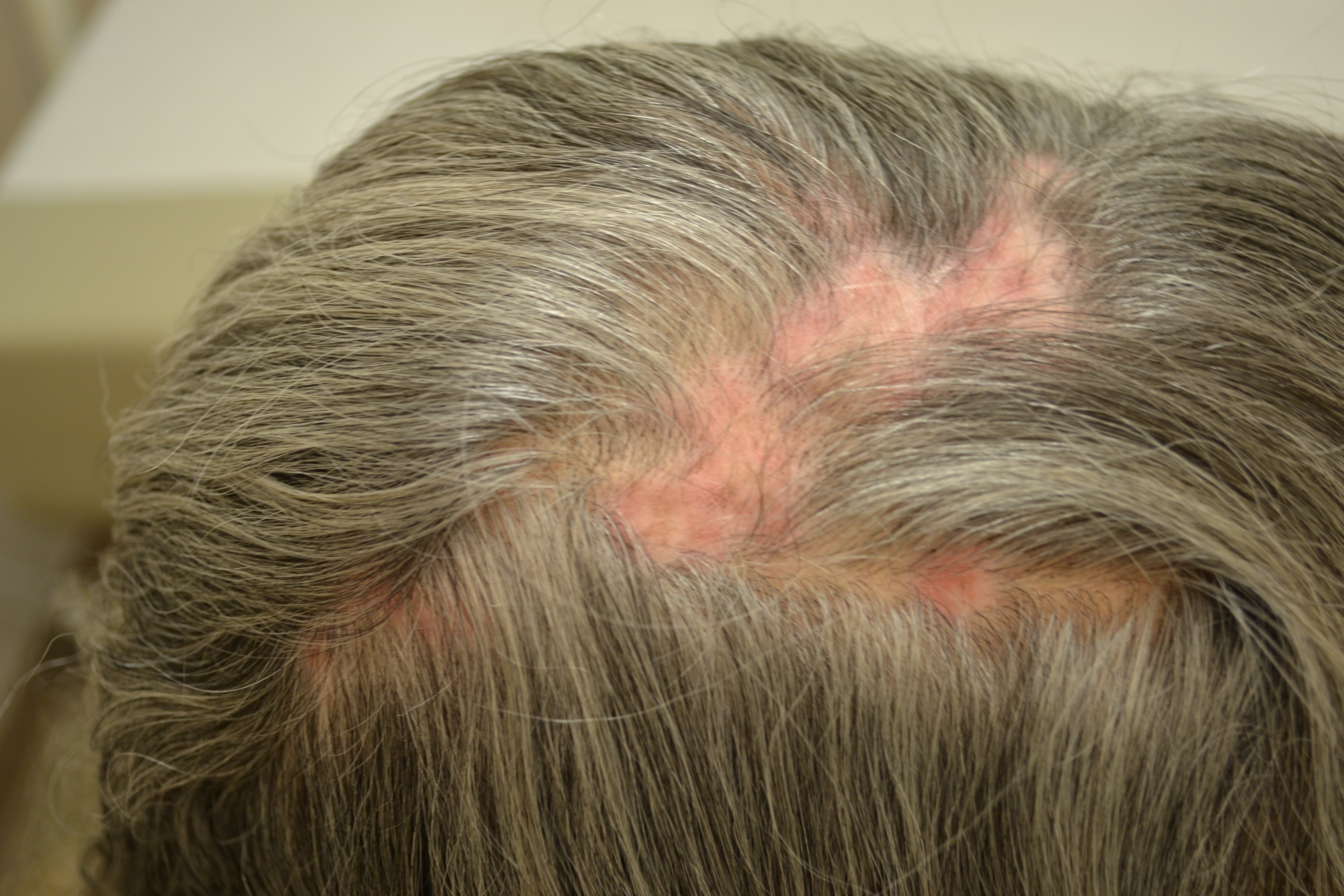
What is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)?
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a type of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the skin and hair follicles. It is characterized by inflammation that surrounds not just the hair follicles but many other structures in the skin. Unlike some forms of hair loss, DLE can potentially be reversed if treated early. However, without early treatment, more than half of the patients may develop permanent scarring alopecia, where hair loss is irreversible.
Symptoms & Causes
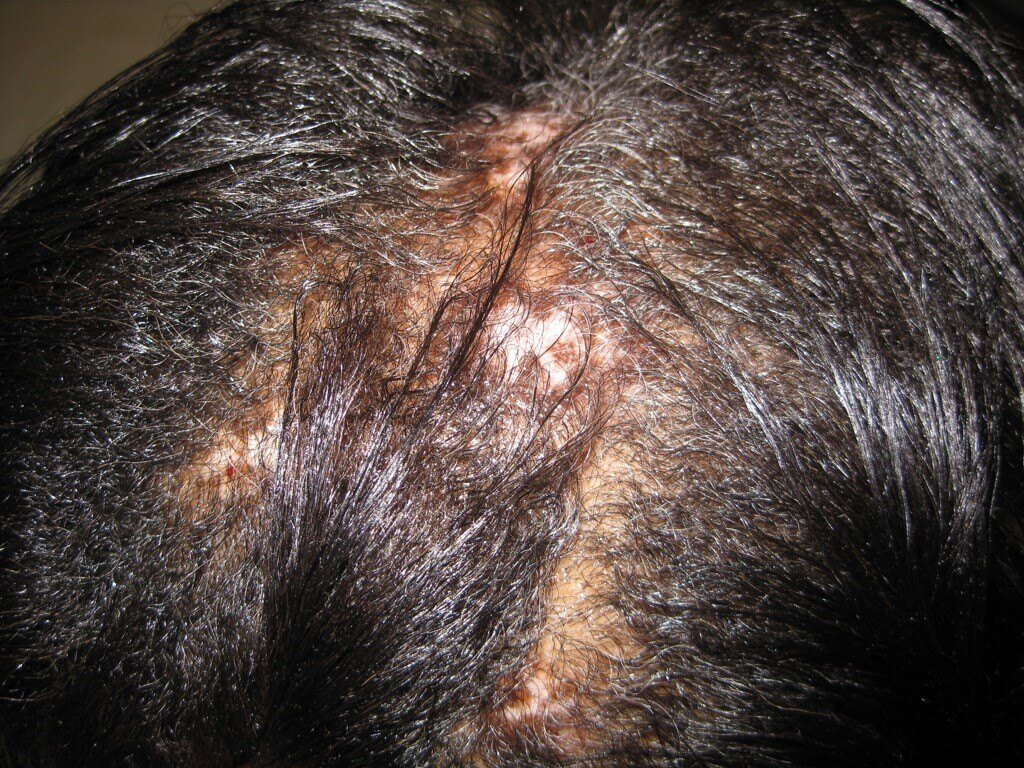
The exact cause of DLE is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic susceptibility, environmental triggers, and other factors, including certain medications and medical conditions. DLE is more common in women, particularly those of African descent, and typically appears between the ages of 20 and 40.
DLE most commonly affects the scalp, face, and ears. It starts as a well-defined, scaly, purplish patch that enlarges into a coin-shaped area of hair loss. These patches can have areas of lighter or darker pigmentation, increased blood vessels, and follicular plugging. A distinctive sign of DLE is the "carpet tack" sign, where lifting the scale reveals spikey keratin underneath. Symptoms may include itching, pain, burning, and tenderness.
Diagnosis & Treatments
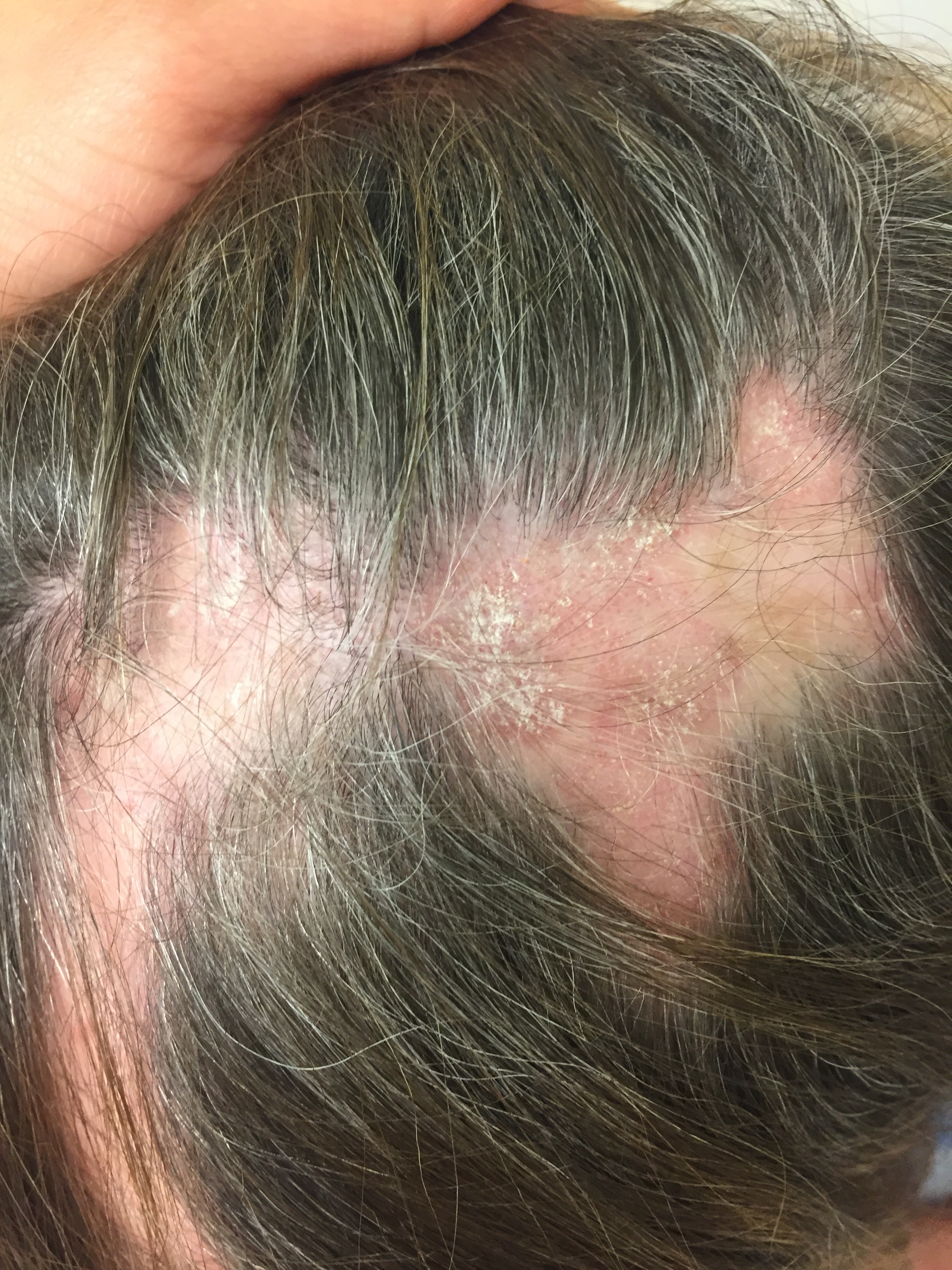
Diagnosing DLE involves a detailed medical history, thorough scalp and skin examination, and scalp biopsies. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent permanent hair follicle damage. Treatments vary based on the severity of symptoms and extent of hair loss.
- Mild Cases: May be managed with topical corticosteroid solutions or foams and topical calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus).
- Moderate to Severe Cases: Often require corticosteroid injections in affected areas, or oral anti-inflammatory medications such as hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) or other anti-malarials, or methotrexate.
- Severe or Resistant Cases: Might need immune suppressant drugs like azathioprine (Imuran), mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept), or cyclosporine.
Since exposure to UV sunlight can trigger or worsen DLE, it is essential to avoid sun exposure and use a broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen if sun exposure cannot be avoided.
For further care, non-surgical options like wigs or hairpieces can help those looking to reduce the visibility of hair loss. Always discuss these options with your dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for you.
